Which Foods Contain Carbohydrates?
The first step in carbohydrate counting is to figure out which foods contain carbohydrates.
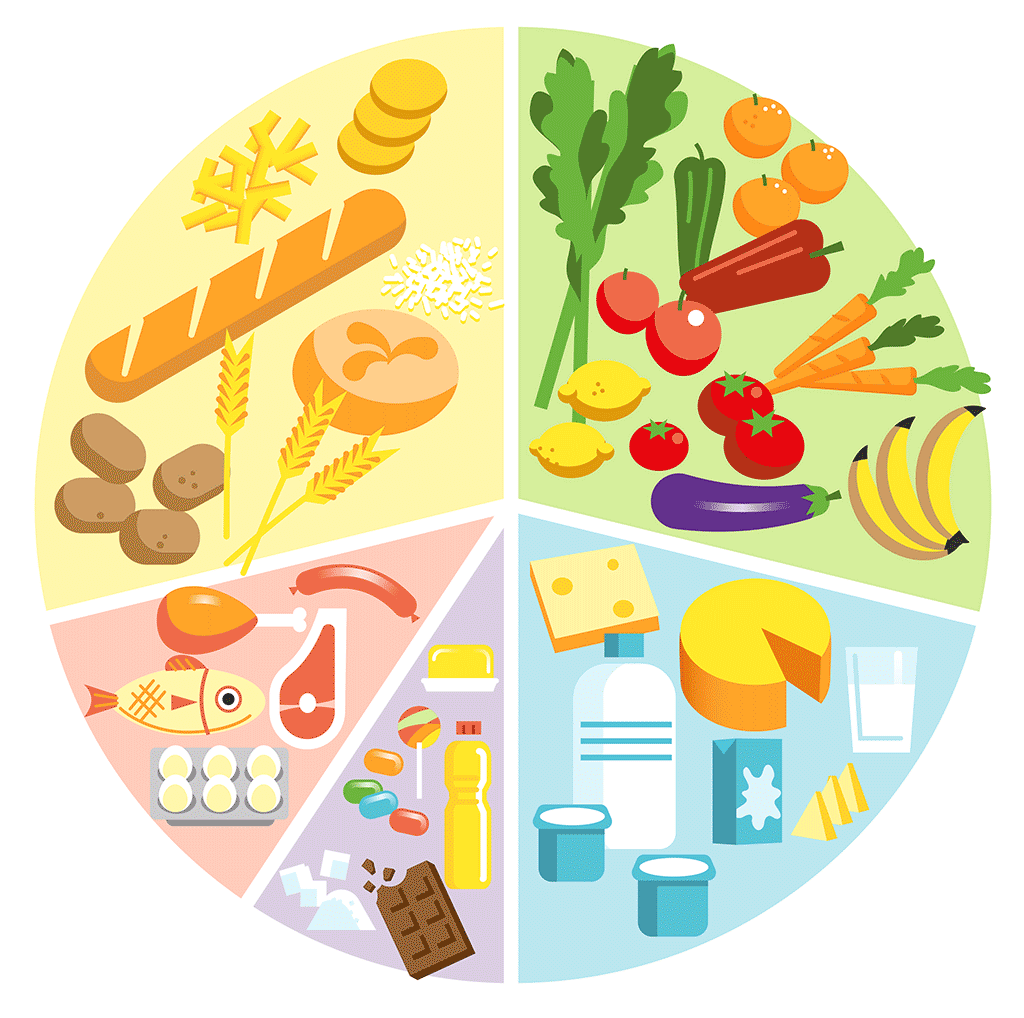
Here’s a list of foods that contain carbohydrates:
- Grains like rice, oatmeal, and barley, freekeh, bulgur, wheat, quinoa, buckwheat…
- Grain and flour based foods like bread, cereal, pasta and crackers, pizza, pastries
- Starchy vegetables like potatoes, sweet potato, and corn
- Fruit and fruit juice
- Milk, yoghurt, laban, kefir
- Legumes like beans, chickpeas, green peas, lentils…
- Soy products like veggie burgers and tofu
- Sweets and snacks like cake, cookies, ice cream, candy, and chips
- Beverages like juices, soft/carbonated drinks, alcohol
Are all carbohydrates the same?
The answer is yes and no. All carbohydrates, no matter the food source, are broken down into glucose and enter the bloodstream. But, depending on the food source, they can have a different effect on glucose levels.
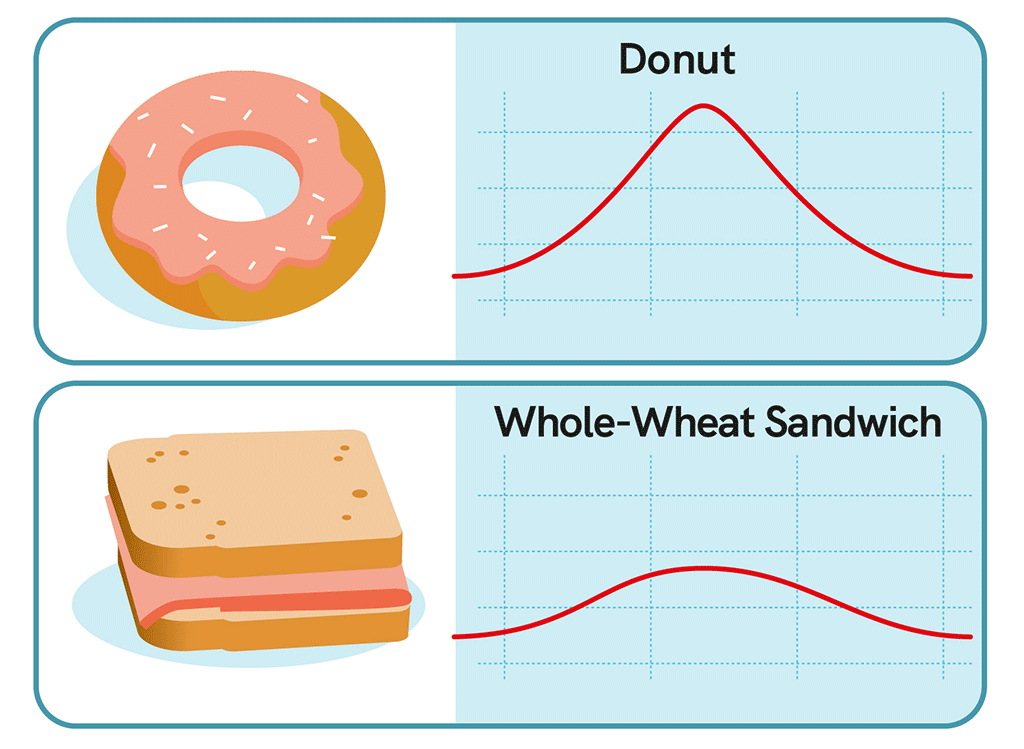
What are the types of carbohydrates?
There are different carbohydrates in our food. In general there are three kinds of carbohydrates; sugars, starches, and fiber.
Sugars
Sugars are classified as simple carbohydrates.
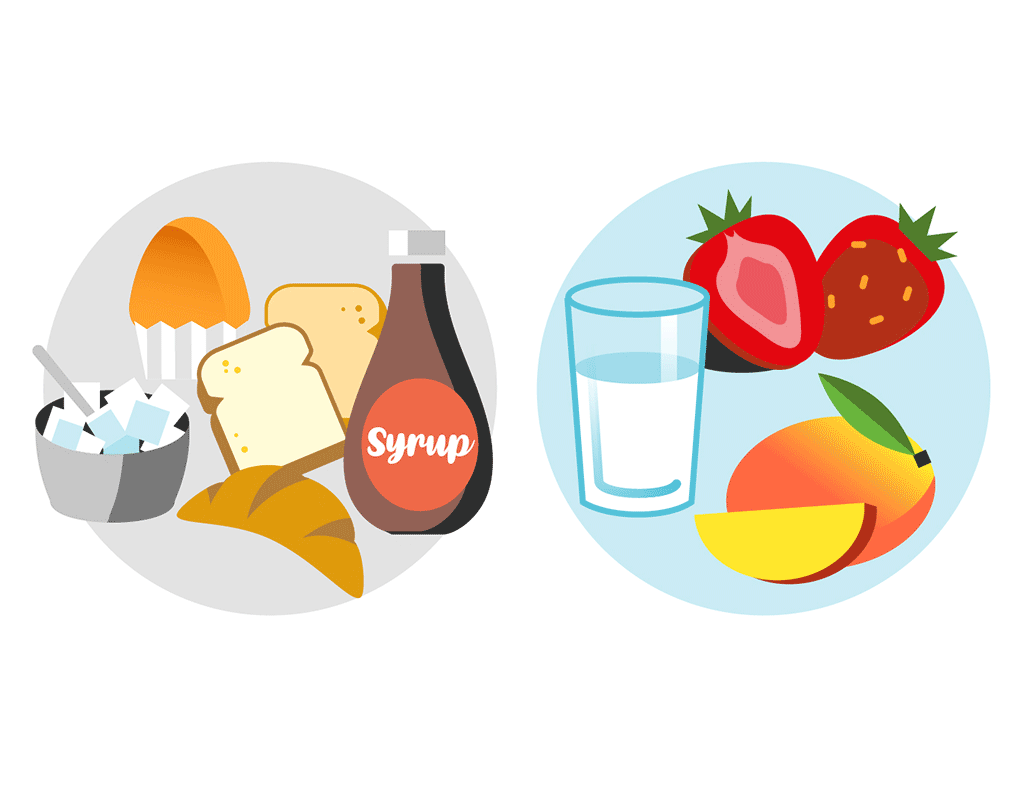
The most familiar sugars are probably processed sugars, like granulated sugar and brown sugar. Sometimes you’ll see these types of sugar listed on food labels as “added sugars”. Then there are the sugars that occur naturally in foods, like fructose in fruits and lactose in milk.
Starches
Starches are classified as complex carbohydrates.
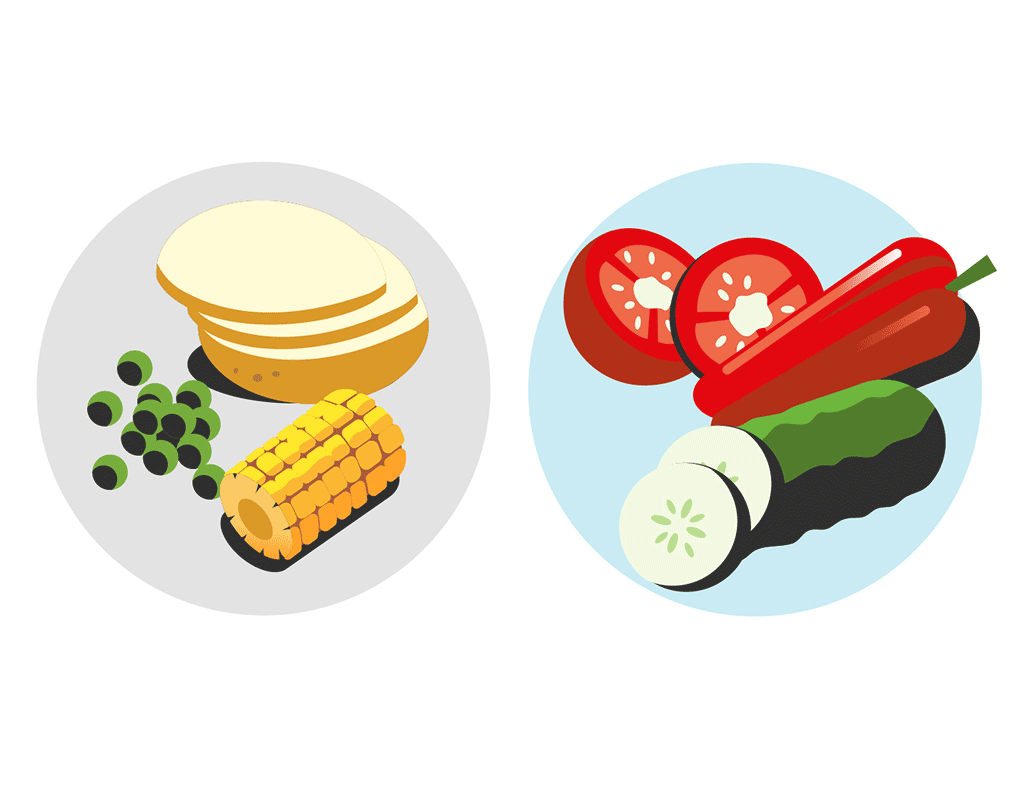
Complex carbohydrates such as legumes, grains, and certain vegetables include high amounts of fiber so they are digested slowly. Therefore, they help to manage blood sugar spikes after meals.
Fiber
Fibers are classified as a type of carbohydrate that the body cannot digest.
This means that instead of being broken down into glucose molecules, fiber passes through the body undigested. Some fiber-rich foods are whole grains, vegetables, seeds and nuts, and some dry fruits. Fiber helps to regulate the body’s use of sugars, slows digestion down, and keeps hunger and blood glucose in check.
Leave a Reply